
¶ Introduction
Open Works has four Boss Laser cutters available to reserve. You must complete a Laser Safety Class before using the machines.
¶ Machine Overview
The Digitial Fabrication Shop's Boss laser cutters use CO2 lasers to cut and engrave a wide variety of materials. Materials placed in the laser cutter may vary in thickness and height, as the bed can be lowered up to approximately 6 inches.
¶ Machines Available
There are four machines available to use.
¶ Machine Comparison
| Number of Machines | Name | Nickname | Power | Bed Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Boss Laser Cutter LS-2436 | Cedar | 60W | 35" x 23" |
| 1 | Boss Laser Cutter LS-2436 | Cypress | 70W | 35" x 23" |
| 2 | Boss Laser Cutter LS-3655 | Spruce & Birch | 100W | 54" x 35" |
You may want to consider tools from the Wood Shop:
| Tool Name | Best For | Worst For |
|---|---|---|
| Band Saw | curved cuts and long cuts | interior cuts and really large pieces |
| Scroll Saw | small pieces, sharp turns, and interior cuts | thick material |
| Jig Saw | large panels and interior cuts | small panels and thick material |
| Laser Cutter | making identical pieces | thick material |
¶ Parts of the Machine
Click to expand
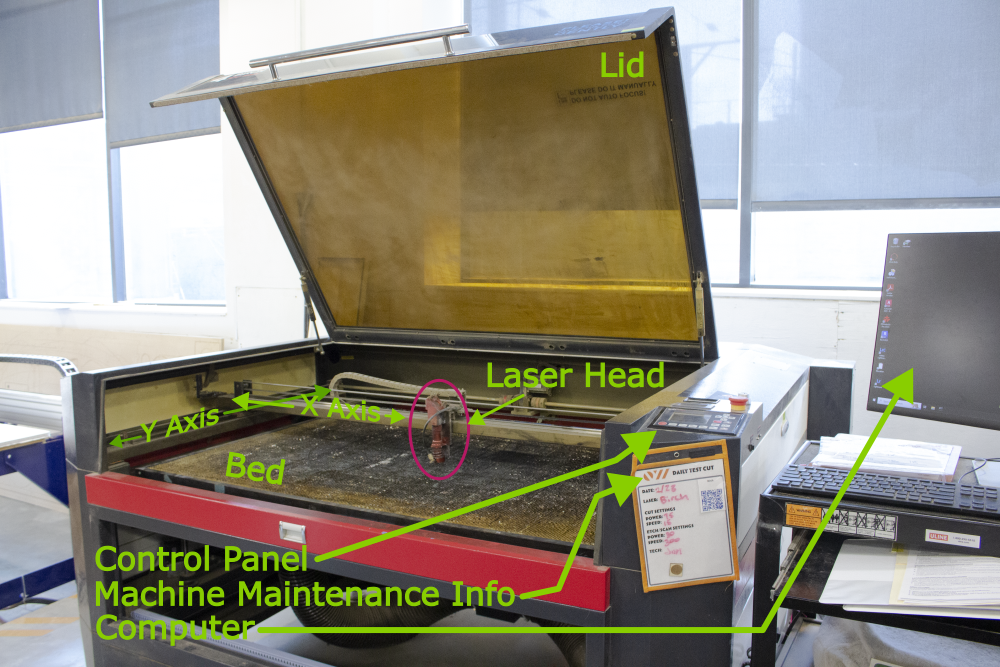
¶ Machine Reservations
You can make machine reservations in the following ways:
Click to expand
- In person at the front desk.
- Reserve a machine any time through our Mind Body Portal.
- Call the front desk during business hours at (410) 862-0424.
- Email us at frontdesk@openworksbmore.com. Please include your name, the machine you'd like to reserve, and the date(s) and times of the reservation(s).
¶ Material Considerations Laser-Safe Materials
¶ Laser-Safe Materials
As listed in the Boss Laser website as of October 2023. For an updated list, go to https://bosslaser.com/laser-safe-materials/.
¶ Plastics:
Acrylic (Also known as Plexiglas, Lucite, PMMA).
Delrin (POM, Acetal).
Kapton Tape (Polyimide).
Mylar (Polyester).
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG).
Two-Toned Acrylic – two-layer colored acrylic, top layer is a different color than the base color. Used for signs, plaques, and instrumentation panels.
¶ Foam:
Depron – Often used for RC planes.
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA).
Gator Foam – Hard shell of gator foam does well but the foam core gets burned and eaten away.
¶ Textiles
Leathers (EXCEPT leather and artificial leather that contains chromium (VI)).
Suede.
Felt.
Hemp.
Cotton.
¶ Other
Paper - Cardstock and cardboard.
Rubber – These can only be used if they do not contain chlorine or Teflon (PTFE, Polytetrafluoroethylene).
Woods – MDF, balsam, birch, poplar, red oak, cherry, holly, etc.
¶ Use with Caution and Proper Technique:
Mirrors.
Nylon – Melts Badly.
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)- Melts Badly.
Polyethylene – Melts Badly.
Polypropylene – Melts somewhat.
Thicker and denser woods.
¶ Forbidden Materials:
DO NOT, under any circumstances, use the following materials in the laser cutter:
Metals (exceptions of etching = Using TherMark. Cutting = HP models “Oxygen/Air assist”
Polycarbonate (PC, Lexan) due to the fumes.
Pleather.
Styrene (Stryrofoam).
Foam Core board.
ABS.
Fiberglass.
Leather and artificial leather that contains chromium (VI).
Carbon fibers (Carbon).
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Polyvinyl butyrale (PVB).
Polytetrafluoroethylenes (PTFE /Teflon).
Beryllium oxide.
Any materials containg chlorine:
PVC (Cintra).
Vinyl.
Any materials containing:
Halogens (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine and astatine).
Epoxy or phenolic resins.
HP (High Pressure) materials include all the above guidelines AND:
Stainless steel up to 18 gauge.
Mild steel up to 20 gauge.
¶ Safety and setup for Laser Cutting
Safety Check:
Sturdy, close-toed shoes must be worn at all times.
Long hair, jewelry, and loose clothing must be tied back.
Safety glasses, earmuffs, and dust mask are recommended while the CNC Router machines are running.
Let the smoke ventilate for a minute or two before opening the lid.
For more information on shop safety visit Digital Fabrication under "Safety."
- Never look directly at the laser.
- Never place hands near the laser or on the bed while the machine is running.
- Never run a cut file with the lid open.
- Know the size of your material - length, width, and depth (thickness). Measuring tape and calipers are available in the tool chest.
- Check the material for warping. If material is warped it should be flattened using tape, scrap wood or weights--check that weights are out of laser head’s way.
- Clear the bed of any extra materials or tools before you begin.
- Verify that your toolpath is clear and will not hit any weights.
- Double check your cut settings in RDWorks.
RISK OF FIRE
If you see a small ember, pause the machine, and open the laser cutter's lid. The air rushing in from opening the lid should snuff out the ember.
There is a water squirt bottle near the laser cutters to squirt any flames.
Notify a Community Technician IMMEDIATELY if any flames remain after opening the lid.
If the fire is still not extinguished and it is safe to do so, pull the workpiece from the laser bed and smother the flame on the concrete floor, or put the workpiece into the fire bin.
If the fire is larger or not easily contained, ask the nearest staff member for assistance.
There are two Co2 fire extinguishers in the Digital Fabrication.
DO NOT begin another cut until the fire is absolutely out, and the laser has been inspected for damage or debris by a Community Technician .
If you feel that you are in danger, pull the fire alarm and advise others in the room to LEAVE. No project or machine is worth your life.
¶ Before You Begin
- Know the fire safety procedures. See 'Risk of Fire' above.
- Have your cut file ready. Have it on a USB key to bring it down to Digital Fabrication from the Computer Lab, or have it on the Member network. Do not do your design on the computer next to the laser cutter.
- Have the machine reserved for the expected duration of the cut(s) + some extra in advance so that you can get the key required to turn the machine on.
- The machine must be turned on in order to download the file to it.
¶ Using the Laser Cutters
It is strongly recommended to do a test cut if you are using a new material or settings, or want to make sure that your trusted material and settings are still working correctly. A test cut follows the same procedure as described below, but the design is typically a simple and quick path such as a square that tests the settings used in the more complex design.
- Put your material in. The piece may need to be secured using grid pins (usually available in DFAB) if it small or could be moved by the air pressure from the ventilation fans. If the piece is warped or not a uniform thickness, you should not use it.
- Turn on the laser cutter.
- Set up the laser cutter:
- Download your cut file to the laser cutter from the computer next to the laser cutter.
- Set the origin.
- Manually focus the laser.
- Close the lid.
- Now you may begin your cut.
¶ Remain with the laser cutter while it performs the cut. Monitor it for problems.
Problems can include fire, material shifting out of alignment, or laser cutter failing to cut as expected. Other problems can occur as well.
Often small bursts of flame appear at the cutting point and go out quickly. This is a part of normal operation.
Fire that does not go out immediately is not normal and must be put out quickly to avoid damage or injury.
¶ If you cannot reach the e-stop, you are not close enough.
You will be asked to remain with the machine. If you are asked multiple times to remain with the machine, you may not be allowed to use the machine.
If you must leave the area (such as to use the bathroom), make sure someone else in the area knows that you have a job running and is observing the machine for you.
¶ Cleaning Up
After the cut is done, wait a minute or two before opening the lid to allow fumes to clear.
When all of your cuts are finished, power off laser cutter by turning the key.
When you’re done working, clean the laser cutter’s bed and vacuum up small pieces.
¶ Maintenance
Find the Maintenance instructions here.
¶ Troubleshooting
Find the Troubleshooting instructions here.
¶ Check Lens Orientation
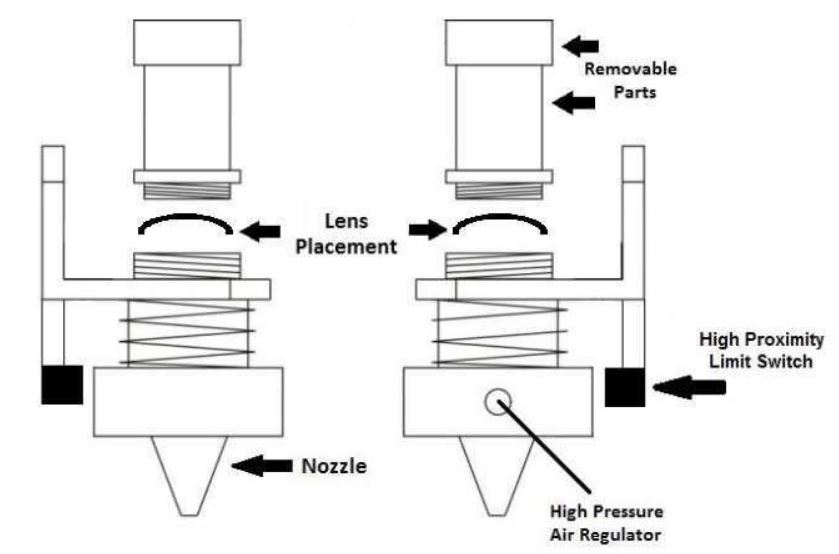
¶ References
Boss manual- Look for LS series manual here
¶ Video Walk Throughs
¶ Glossary
Chiller: A water-cooling machine that prevents the laser cutter from overheating which must be turned on whenever the laser cutter is in use.
CNC (Computer Numerically Controlled machine): The laser utilizes vectors,or curves—lines with directional and coordinate information—to guide a concentrated and focused laser beam to cut through materials.
CO2 gas laser: The laser cutter contains a tube filled with a cocktail of gases, and which uses electricity to produce an infrared light. The ends of the tube are mirrors; one of which is fully reflective and the other which lets some light through.
Cut: A cut is when the laser is used to follow a path, penetrating completely through the material. Usually the path followed is closed so the material within the path falls out.
Engrave A process in which the laser burns the material, column by column, with a bitmap—a grid of dots (or pixels). The laser cutter uses the resolution information in the bitmap to know how far apart mark the dots, both within the columns and distance between the columns. Used typically to render photographs. See Scan.
Graphics- Raster vs Vector: Raster graphics are composed of pixels, while vector graphics are composed of paths.
Kerf: The laser burns away a portion of material when it cuts through. This is known as the laser kerf, and ranges from 0.08mm – 1mm depending on the material type and other conditional factors. The width of this kerf can depend on the thickness of material, heat and speed of the cut.
Scan: A process by which the laser burns shallow passes, column by column, across the material from a vector. The effect is cleaner but appears more digital than engraving. See Engrave.
Zero: (home, origin): The starting point or "home" for each axis on a digital fabrication machine.